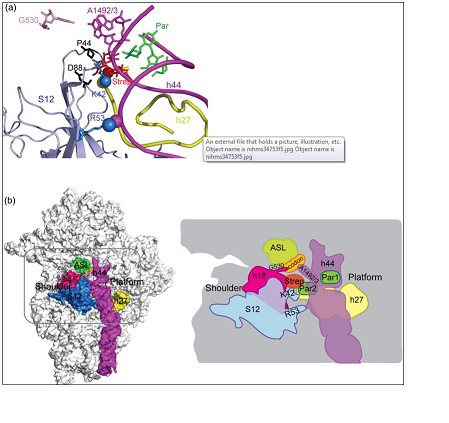
Streptomycin is an antibiotic that disrupts the 30S subunit of the E. coli (W3110) ribosome. A mutation in this gene (rpsL) results in three viable phenotypes: Streptomycin resistant (StrR), Streptomycin dependent (StrD) and Streptomycin intermediate (StrI). The spontaneous mutation frequency of StrR mutants was 3.0 x 10-9 mutants/viable cells and <6.0 x 10-10 mutants/viable cells for StrI and 6.0 x 10-10 for StrD mutants. The BlastN, BlastX and Multalin bioinformatics tools revealed that a change of the 43rd amino acid from lysine to asparagine results in the StrR phenotype, while a change of the 91st amino acid from proline to leucine results in the StrI phenotype. No StrD data were present.